
Loss of a pregnancy before the 20th week is termed miscarriage. Affecting 10-15% of confirmed pregnancies, it often occurs due to natural causes like chromosomal abnormalities, hormonal imbalances, or maternal health issues.
Understanding Miscarriage: Causes, Symptoms & When to Seek Help
Understanding Miscarriage: Causes, Symptoms & When to Seek Help
Let’s talk about miscarriage—what causes it, warning signs, and when to consult a doctor during early pregnancy.
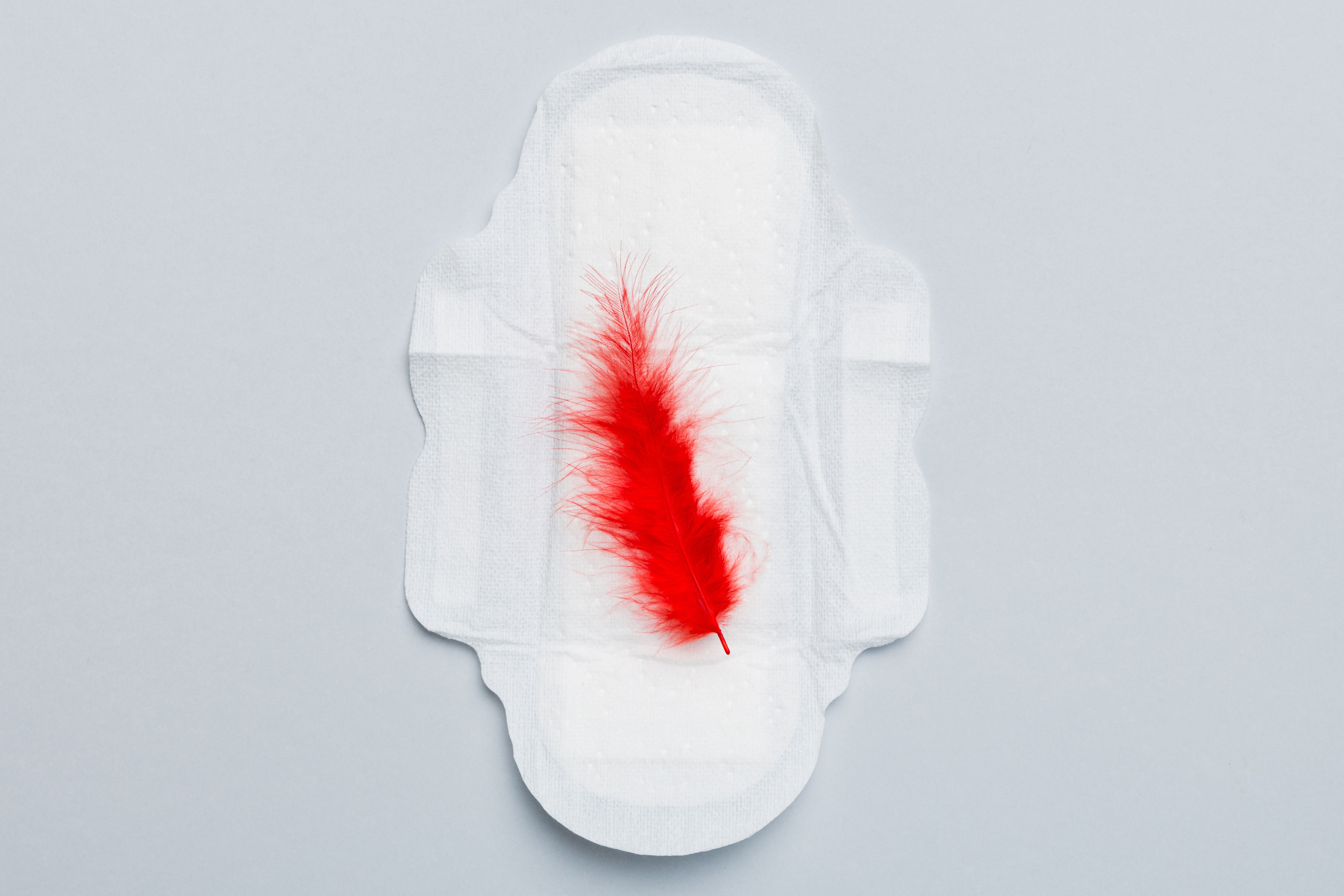
Recognizing miscarriage symptoms is crucial. Common signs include vaginal bleeding, cramps, blood clots, and reduced pregnancy symptoms like nausea or breast tenderness.

Here are some of the signs of early miscarriage to watch for:
Miscarriage can occur in various forms, each with distinct symptoms and causes. Two common miscarriage types include threatened miscarriage and missed abortion.
A threatened miscarriage or threatened abortion refers to symptoms that suggest a possible pregnancy loss but that's not the case necessarily. These may include vaginal bleeding or mild abdominal cramps during early pregnancy. Despite these symptoms, the foetus often remains viable, and timely medical care can help manage the situation.
A missed abortion occurs when the foetus stops developing, but there are no immediate symptoms such as bleeding or cramping. The pregnancy may be lost without the mother experiencing any signs.
In contrast, a threatened abortion involves symptoms like vaginal bleeding or abdominal cramps, which suggest a risk of miscarriage. However, the pregnancy may still continue and remain viable with appropriate medical care.
Miscarriages can occur for various reasons including chromosomal abnormalities, maternal health issues, uterine problems, infections, dietary concerns and lifestyle factors.

Chromosomal abnormalities, often out of the parent's control, account for up to 50-60% of cases. These occur when the foetus has incorrect chromosomes, leading to developmental issues.
Maternal health conditions like diabetes, thyroid disorders, and hormonal imbalances can increase the risk of miscarriage. Uterine issues such as fibroids or structural abnormalities can also hinder fetal development.
When eaten in moderation, most everyday foods are safe for pregnancy and unlikely to cause harm.
Many women worry about everyday activities or habits leading to miscarriage, but it’s important to separate facts from myths. Here are some common misconceptions clarified:

Avoid Henna
Avoid hair dyes that contain henna because they could increase the risk of miscarriage.

Healing time
Rest as much as possible by staying in bed to help your body reach complete recovery.

No To Papaya
Avoid Papaya containing canned mixed fruit juice, as it can cause miscarriage.

Support circle
Embrace the emotional support from family and friends to help you through tough moments.

Doctor Checkin
To get a clear understanding of medication and surgical risks, always consult your doctor.

Butter Can Help
Rub unsalted butter on your lower abdomen to help prevent miscarriage during pregnancy.

Ring your Doctor
Don’t self-medicate during a miscarriage, consult your doctor for proper guidance and care

Early warning
Spotting or bleeding can be an early sign of miscarriage, watch out for signs to seek help
Miscarriage bleeding varies based on your pregnancy stage. It may begin as spotting and progress to heavier miscarriage blood with clots. Always consult your doctor if in doubt.
Taking the right precautions during early pregnancy can significantly reduce the risk of miscarriage. Here are some key steps to follow for a safe and healthy pregnancy:
If you are concerned about miscarriage, it’s important to consult your doctor for personalised advice. They may recommend:
The D&C procedure for miscarriage is performed to remove pregnancy tissue and clean the uterus. Bleeding typically lasts 1-2 weeks after the procedure, though it may vary. To support recovery, focus on rest, hydration, and a healthy diet.
Miscarriage risk is highest in the first 8 weeks. After detecting a fetal heartbeat, the risk drops significantly and decreases further after 12 weeks.

It is a genetic screening used to identify chromosomal abnormalities. It is especially recommended after recurrent miscarriages to determine if genetic issues are involved.
For most women, with proper care and guidance, pregnancy after miscarriage is still possible. Here's what you need to know:

Discover trusted advice from experts for all stages of your parenting
Your recovery matters. Discover key tests to help you heal, recharge, and stay healthy.
FAQs
Most miscarriages occur within the first 8–10 weeks of pregnancy, during the critical period when the baby’s organs are developing. Many of these are due to chromosomal abnormalities that prevent proper development.
To lower the risk of miscarriage, focus on prenatal care, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking, alcohol, and excessive caffeine. Regular medical check-ups and managing chronic conditions can also help ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Heavy bleeding with clots, severe cramping, and the loss of pregnancy symptoms may indicate a miscarriage. However, only a doctor can confirm it through medical tests or an ultrasound. So seeking medical advice is essential.
Waiting three months after a miscarriage allows your body to recover fully and ensures your uterine lining is healthy. It also provides time to address any health concerns and prepare emotionally for a new pregnancy.
Most people wait until after the 12-week mark, as the risk of miscarriage decreases significantly by then. This timing also allows for initial medical tests and greater confidence in sharing the news.