Psychotherapeutic Treatments for Postpartum Depression
Psychotherapy, or talk therapy, is the cornerstone of PPD treatment. It provides mothers with emotional support and coping strategies, helping them manage the stress and emotional toll of facing new motherhood. Through therapy, mothers can develop strategies to manage the overwhelming emotions often experienced during this period.
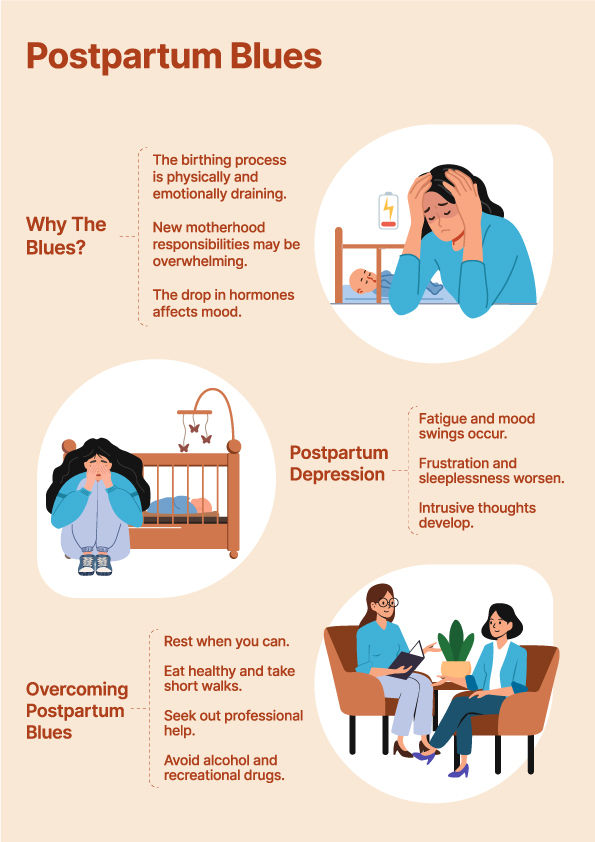
Common causes of PPD include hormonal changes, sleep deprivation, and the emotional strain of caring for a newborn. By addressing these causes, psychotherapy helps postpartum mothers better understand their emotions and regain control of their mental well-being.
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) and Interpersonal Therapy (IPT) are two effective therapeutic approaches used to treat postpartum depression. Both help mothers recognise negative thought patterns, improve their relationships, and develop healthy coping mechanisms.
Cognitive-Behavioural Therapy
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) is highly effective in treating PPD. This therapy works by helping mothers recognise and challenge negative thoughts, replacing them with positive coping mechanisms. CBT involves:
- Identifying patterns of thought that lead to feelings of depression
- Learning strategies to cope with overwhelming emotions
- Developing skills to break the cycle of negative thinking
CBT is widely practised in India, and many healthcare professionals recommend it as part of postpartum depression treatment.
Interpersonal Therapy
Interpersonal therapy (IPT) focuses on improving relationships and communication. It addresses interpersonal conflicts, role transitions, and social isolation, all common issues for new mothers. It helps mothers:
- Rebuild relationships with family members
- Develop a stronger support system
- Improve communication with their partner
IPT is often used for mothers who feel disconnected from their loved ones during the postpartum period.