General Health
Skincare Routine For Acne-Prone Skin
By Apollo Pharmacy, Published on- 01 February 2024, Updated on -06 August 2024
Share this article
0
0 like
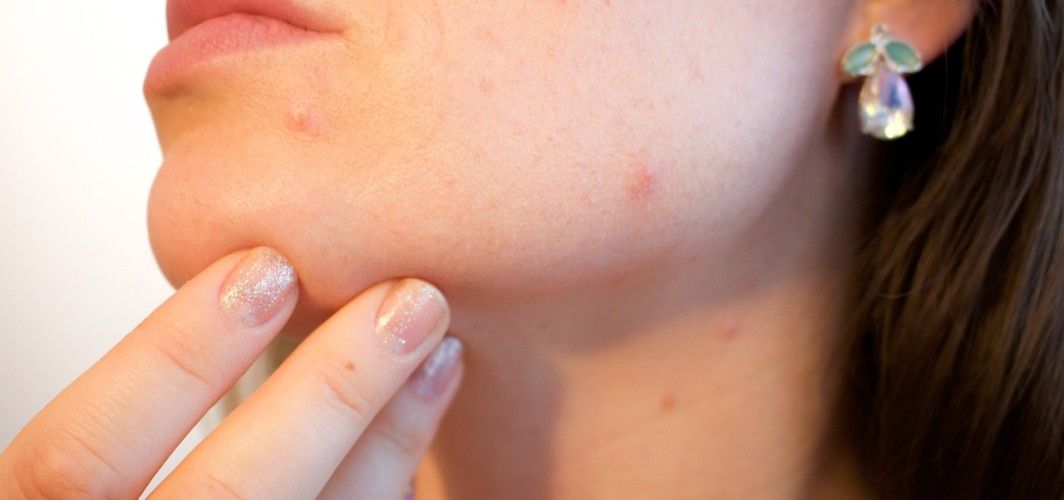
Acne-prone skin refers to a skin type that is predisposed to developing acne, characterized by the formation of pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and sometimes deeper cysts. This condition often requires a targeted skincare approach to manage and prevent breakouts effectively. Acne can be attributed to various factors, including excess oil production (sebum), clogged pores, bacteria (Propionibacterium acnes), hormonal fluctuations, and inflammation. Establishing a daily skin care routine at home is paramount for individuals with acne-prone skin. A consistent and well-crafted skincare regimen outlines how to take care of skin and can help address the underlying causes of acne and promote clear, healthy skin.
Understanding Acne-Prone Skin
Acne-prone skin is characterized by an increased susceptibility to developing acne, a common skin condition. Understanding the characteristics of acne-prone skin can help individuals prevent breakouts.
Characteristics of Acne-Prone Skin
- Excess sebum production: Sebum is an oily substance produced by the sebaceous glands in the skin. People with acne-prone skin tend to produce an excessive amount of sebum, leading to clogged pores and breakouts.
- Increased keratinization: In acne-prone individuals, the process of keratinization, where dead skin cells shed from the surface of the skin, becomes imbalanced. This can result in the accumulation of dead skin cells within hair follicles, contributing to the formation of comedones (blackheads and whiteheads).
- Bacterial colonization: The presence of Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) bacteria on the skin is normal but can become problematic in individuals with acne-prone skin. The proliferation of this bacteria within clogged pores can lead to inflammation and trigger the development of acne lesions like papules, pustules, and nodules.
Identifying Different Types of Acne
Acne manifests in various forms, and recognising these different types is essential for targeted treatment.
- Pimples: Small, raised bumps on the skin often containing pus. These can be further categorized into whiteheads and blackheads.
- Whiteheads: Closed comedones, or clogged pores, appear as small, flesh-coloured bumps on the skin.
- Blackheads: Open comedones, where the pore is open, allowing the trapped sebum and dead skin cells to oxidize and turn black.
- Cysts: Deeper, painful lesions filled with pus that can lead to scarring if not treated appropriately.
Preparing Your Skincare Routine
Here are some things to consider while preparing a skincare routine for your acne-prone skin.
1. Consultation With a Dermatologist
When it comes to skincare, seeking professional advice from a dermatologist is crucial. Dermatologists can evaluate your skin type, identify any underlying conditions, and recommend personalized skincare routines tailored to your specific needs.
Consulting a dermatologist is especially important if you have specific concerns such as acne, rosacea, or eczema. These conditions may require specialized treatments that only a professional can provide.
2. Know About Different Skin Types
When it comes to skincare, understanding your skin type is crucial because different skin types have different needs and require specific care. There are three main skin types: oily, dry, and combination.
- Oily skin: If your skin tends to be shiny and greasy throughout the day, especially around the middle of your face, you likely have oily skin. Oily skin is characterized by excessive sebum production, which can lead to clogged pores and acne breakouts.
- Dry skin: Dry skin often feels tight and rough, and may appear flaky or scaly. It is caused by a lack of moisture in the skin, resulting in a weakened moisture barrier that struggles to retain water.
- Combination skin: Combination skin is when you have both oily and dry areas on your face. Typically, the T-zone (forehead, nose, and chin) tends to be oily, while the cheeks are drier.
3. How to Determine Your Skin Type?
Steps to check your skin type:
- Cleanse your face: Start with a gentle cleanser to remove any dirt or makeup from your face. Pat dry with a clean towel.
- Wait for an hour: Allow your skin to return to its natural state without applying any skincare products or touching your face during this time.
- Assess shine and texture: After an hour has passed, observe how your skin looks and feels.
Match with these results:
- Oily skin: If your face appears shiny all over and feels greasy to the touch, you most likely have oily skin.
- Dry skin: If your face feels tight, looks flaky or rough, and lacks shine or oiliness, you probably have dry skin.
- Combination Skin: If some areas of your face feel oily while others feel dry or normal, then you have combination skin.
4. Assessing Sensitivity Levels
Understanding the sensitivity of your skin is essential for choosing gentle and soothing products. A patch test conducted by a dermatologist can help assess sensitivity levels, guiding the selection of products that minimize the risk of irritation.
Cleansing for Acne-Prone Skin
Choosing gentle cleansers is paramount for acne-prone skin in daily skin care routine at home, as harsh products can exacerbate irritation and disrupt the skin's natural balance. Gentle cleansers effectively remove impurities without stripping the skin of essential oils.
1. Recommended Ingredients for Acne-Prone Skin
Here are some recommended ingredients for acne-prone skin:
- Salicylic Acid: Salicylic acid is a beta-hydroxy acid renowned for its ability to exfoliate and unclog pores. It helps remove excess oil and dead skin cells, preventing the formation of acne lesions.
- Tea Tree Oil: Tea tree oil possesses antimicrobial properties, making it effective against acne-causing bacteria. It can aid in reducing inflammation and promoting clearer skin.
- Neem Extract: Neem extract is known for its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. Including neem in cleansers can contribute to the overall health of acne-prone skin.
Step-By-Step Cleansing Routine
- Washing Face Twice Daily: Establishing a consistent routine by washing your face twice a day – in the morning and evening – is a fundamental practice in learning how to take care of skin. This helps remove accumulated impurities and prepares the skin for subsequent skincare steps.
- Avoiding Harsh Scrubbing: Gentle cleansing involves avoiding harsh scrubbing, which can irritate the skin and exacerbate acne. Instead, opt for soft, circular motions to cleanse without causing unnecessary friction.
Exfoliation and Toning
Regular exfoliation is crucial for acne-prone skin in a daily skin care routine at home as it helps in the removal of dead skin cells, preventing the clogging of pores and reducing the risk of acne breakouts. Additionally, exfoliation promotes cell turnover, contributing to a smoother and more radiant skin texture.
1. Suitable Exfoliating Agents
Here are two suitable exfoliating agents to consider:
- AHAs (Alpha Hydroxy Acids): AHAs, such as glycolic acid and lactic acid, are effective exfoliants that work on the skin's surface. They help in loosening and removing dead skin cells, promoting a brighter complexion.
- BHAs (Beta Hydroxy Acids): BHAs, like salicylic acid, penetrate deeper into the pores, making them especially beneficial for acne-prone skin. They help dissolve excess sebum, unclog pores, and reduce inflammation.
2. Importance of Toning
Toning plays a crucial role in the skincare routine for acne-prone skin, offering several advantages.
- Balancing pH Levels: Toning helps balance the skin's pH levels, creating an environment that is less favorable for the growth of acne-causing bacteria.
- Tightening Pores: Toners containing ingredients like witch hazel or chamomile can help tighten pores, reducing their appearance and minimizing the risk of debris and oil accumulation.
Moisturizing and Sun Protection
Moisturizing and sun protection are pivotal aspects of a comprehensive skincare routine for acne-prone skin.
1. Hydration for Acne-Prone Skin
Here are some tips for hydrating acne-prone skin:
- Non-Comedogenic Moisturizers: Look for moisturizers labeled as non-comedogenic, which means they are formulated to not clog pores. These moisturizers are less likely to exacerbate acne breakouts.
- Recommended Ingredients: Hyaluronic acid is an excellent ingredient for moisturizing acne-prone skin. It is a humectant that helps to draw moisture into the skin, keeping it hydrated without adding excess oil or causing breakouts. Other beneficial ingredients include ceramides, glycerin, and niacinamide.
2. Importance of Sunscreen for Acne-Prone Skin
The Indian subcontinent experiences high levels of UV radiation throughout the year, making it essential to wear sunscreen daily. Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 to protect against both UVA and UVB rays.
Acne-prone skin can be sensitive and easily irritated by heavy or greasy formulas. Opt for oil-free or gel-based sunscreens that are lightweight and won't clog pores. Look for labels indicating "non-comedogenic" or "oil-free".
How to Treat Acne?
Effectively treating acne involves a multi-faceted approach, including over-the-counter options and, when necessary, prescription medications.
1. Over-The-Counter Treatments
Here are two effective over-the-counter treatments for managing acne:
Benzoyl Peroxide: Benzoyl peroxide is a widely used over-the-counter treatment that works by reducing acne-causing bacteria and preventing the formation of new blemishes. It is available in various formulations, including cleansers, creams, and gels.
Retinoids: Over-the-counter retinoid products, such as those containing adapalene, play a crucial role in promoting skin cell turnover. They help unclog pores, reduce inflammation, and improve the overall texture of the skin.
2. Prescription Medications
Here are two prescription medications for managing acne:
- Topical Antibiotics: In cases where acne is associated with bacterial infection, topical antibiotics like clindamycin or erythromycin may be prescribed. These medications help control bacterial growth and reduce inflammation.
- Oral Contraceptives: Hormonal imbalance can contribute to acne, especially in women. Oral contraceptives help regulate hormonal imbalances, leading to a reduction in hormonal acne.
Lifestyle and Dietary Considerations
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial in learning how to take care of skin. Adequate sleep, stress management, and regular exercise play crucial roles in managing acne-prone skin.
1. Foods to Avoid for Acne-Prone Skin
- Highly Processed Foods: Reduce intake of heavily processed foods, as they may contribute to inflammation and exacerbate acne.
Dairy Products: Some individuals may experience severe acne after consuming dairy. Consider limiting dairy or opting for dairy alternatives such as almond milk. - High-Glycemic Foods: Foods with a high glycemic index, such as sugary snacks and refined carbohydrates, can influence acne. Choose complex carbohydrates such as oats, whole grains and cruciferous vegetables for a more stable blood sugar level.
2. Foods to Include in Your Diet
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Incorporating a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables into your diet provides antioxidants that help protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals. Examples include berries, citrus fruits, leafy greens, and bell peppers.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Include sources of omega-3 fatty acids like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts. These can help reduce inflammation and support skin health.
- Probiotic-Rich Foods: Probiotics found in yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods contribute to a healthy gut, potentially impacting skin conditions.
Additional Tips and Precautions
Here are some additional tips and precautions for managing acne-prone skin:
1. Avoiding Picking or Popping Pimples
Succumbing to the temptation of picking or popping pimples can lead to increased inflammation, scarring, and the spread of bacteria. Resist the urge, and instead, focus on a consistent daily skin care routine at home to address and prevent breakouts.
2. Managing Stress Levels
Chronic stress can exacerbate acne by triggering hormonal fluctuations. Incorporate stress management techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or regular exercise into your routine to promote overall well-being and contribute to clearer skin.
3. Regularly Cleaning Makeup Brushes
Makeup brushes can harbor bacteria and contribute to clogged pores. Regularly clean your brushes to prevent the transfer of bacteria onto your skin. Use a gentle cleanser and allow the brushes to dry thoroughly before their next use.
Conclusion
From gentle cleansing, exfoliation, and hydration to incorporating over-the-counter and prescription treatments, each step contributes to managing breakouts and promoting healthier skin. A daily skin care routine at home designed for acne-prone skin is a proactive and effective way to address specific concerns and learn how to take care of skin.
General Health
Frequently asked questions
No, moisturizing is crucial for acne-prone skin. Opt for non-comedogenic moisturizers to maintain hydration without clogging pores.
Exfoliation frequency varies, but generally, 2 times a week is sufficient. Over-exfoliating can irritate the skin and worsen acne.
Yes, you can wear makeup, but choose non-comedogenic and oil-free formulas. Ensure you remove makeup thoroughly at the end of the day, and regularly clean your brushes to prevent bacterial buildup, a common cause of breakouts.
Some natural remedies can be beneficial, but their effectiveness varies. Tea tree oil, aloe vera, and honey possess antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. However, it's essential to consult with a dermatologist to ensure these remedies complement your overall skincare routine.
Yes, hormonal changes can influence acne. For women, hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle can contribute to breakouts. Consult with a dermatologist to explore suitable options for hormonal acne management.
Leave Comment
Recommended for you
General Health
How To Use Prega News? A Guide For Early Pregnancy Detection
Discover the power of Prega News for early pregnancy detection. Explore its usage, result interpretation, and benefits, empowering yourself for a confident pregnancy journey.

General Health
How To Increase Hemoglobin? Know 6 Ways To Improve Your Levels
This blog highlights the significance of hemoglobin in the body and provides effective strategies to increase hemoglobin levels naturally. It explains the role of hemoglobin in oxygen transportation, carbon dioxide removal, and pH regulation. It also discusses the symptoms and causes of low hemoglobin levels and suggests dietary changes to boost hemoglobin.
.jpg?tr=q-80)
General Health
What is Alkasol Syrup: Indications, Benefits, and Action
Alkasol Syrup can offer you relief from UTIs, kidney stones & high uric acid by balancing urine pH. Learn its uses, benefits, dosage & precautions.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.
