- Home
- Blog
- General Health
White Lung Pneumonia: The New Respiratory Illness In Kids
General Health
White Lung Pneumonia: The New Respiratory Illness In Kids
By Apollo Pharmacy, Published on- 08 December 2023, Updated on -19 September 2024
Share this article
0
7 likes
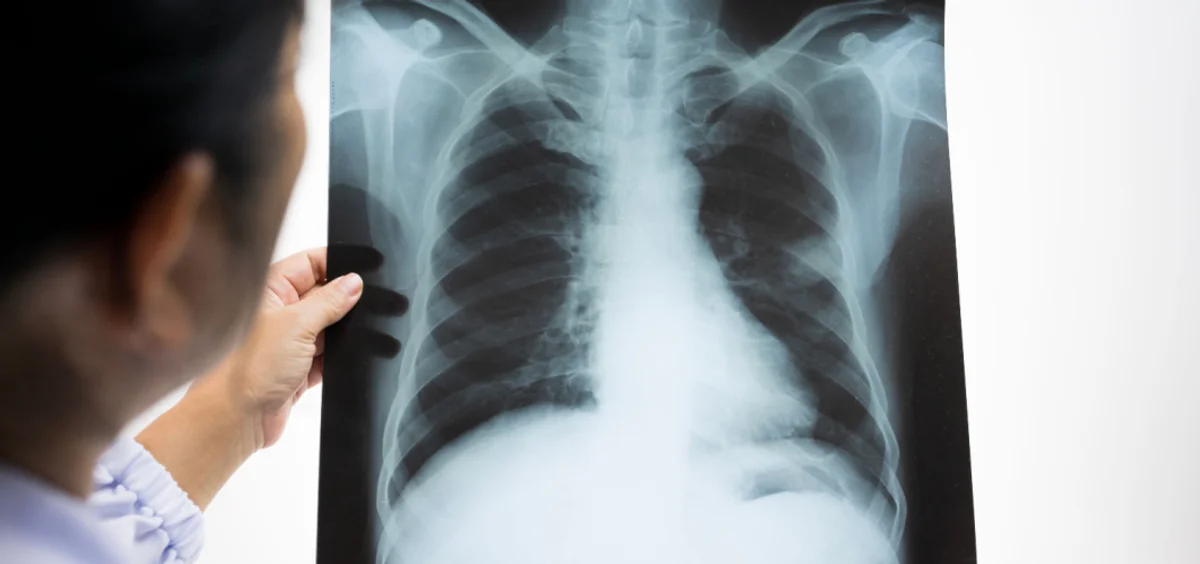
A respiratory disease in northern China and Ohio, known as the White Lung Pneumonia, has led to speculation about a potential disease outbreak. The pneumonia affects children of age 3 to 8 causing an increase in respiratory illness in children. Reports indicate that the white lung pneumonia outbreak in China could be the result of a new strain of Mycoplasma pneumoniae, which is a bacterium that is resistant to many antibiotics. In this blog, we’ll know more about this disease and how it can affect the health of children.
What is White Lung Pneumonia?
White Lung Pneumonia is a respiratory infection in which the lung tissue presents as opaque, white patches on an x-ray. Though it's not a medical term, it simply represents a type of pneumonia which exhibits white patches on the x-ray. Microbes that may result in white lung pneumonia include Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), Adenovirus, Influenza virus and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2).
Symptoms of White Lung Pneumonia
Symptoms of White Lung Pneumonia vary depending on the cause, but typical indicators include:
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing
- Chest pain
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Phlegm accumulation in the sinuses (empty spaces in the body)
- Runny nose
- Nausea
If someone is experiencing these symptoms, make sure to see a healthcare professional to confirm the diagnosis.
Causes of White Lung Pneumonia
Experts are trying to figure out the exact cause of White Lung Pneumonia but it can be either due to individual or a combination of bacterial, viral and environmental factors.
- Viruses: White Lung Pneumonia can be caused by viruses like influenza, RSV, or COVID-19, which cause damage to the air sacs in the lungs.
- Bacteria: Bacterial infections like those caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae and Mycoplasma pneumoniae may also induce pneumonia by triggering lung infections.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental factors including inhaling silica dust and other pollutants also induce White Lung Pneumonia by irritating the lungs, making them susceptible to infections.
Diagnosis of White Lung Pneumonia
The White Lung Pneumonia can be diagnosed by taking imaging scans, including:
- Chest X-ray: Chest X-rays produce images of your lungs and airways using a small dose of radiation. It can also reveal fluid in or around your lungs or air surrounding a lung.
- CT scan: A computerised tomography (CT) scan combines a series of X-ray images taken from different angles around your body. CT scan images provide more detailed information than plain X-rays do.
Treatment for White Lung Pneumonia
The treatment of White Lung Pneumonia depends on the underlying cause of the pneumonia. However, the following methods can be followed generally:
- Nebulisation: Nebulizers may help in easy inhalation of medication, thus providing immediate relief.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are recommended to fight bacteria by killing them or inhibiting their growth.
- Antiviral Medicine: Antiviral medications can ease symptoms and shorten the length of a viral infection.
- Oxygen Therapy: Also called supplemental oxygen, it provides you with extra oxygen to breathe in. Medical ventilation may be required in severe cases.
- Corticosteroids: Steroids are used to reduce inflammation (swelling) and mucus buildup in the airways of the lungs.
NOTE: Be sure to seek medical help instead of doing self-treatment.
Prevention of White Lung Pneumonia
To prevent White Lung Pneumonia it is important to take preventive measures such as:
- Hand Washing: Clean hands with soap/hand wash and water to remove any viruses, bacteria, microorganisms, dirt, grease, or other harmful substances.
- Covering Mouths When Coughing: It is advisable to cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or handkerchief when coughing or sneezing to reduce the spread of germs.
- Stay at Home if Sick: Staying indoors when you are sick and not engaging with others helps to not spread the infection to others.
- Taking Vaccinations: It is recommended to take vaccinations for influenza, COVID-19 and other respiratory pathogens to reduce the risk of getting an infectious disease.
- Physical Distancing: Keep a physical distance of at least 1 metre from others, and avoid crowds and close contact to prevent infection spread.
- Avoid Smoking: Exposure to tobacco smoke suppresses the activation of innate immune responses to bacterial infection.
- Wear Masks: Wear a properly fitted mask like N95 and N99 masks in crowded places and poorly ventilated settings to avoid getting any infectious diseases.
Complications of White Lung Pneumonia
Complications of White Lung Pneumonia will vary depending on the underlying cause. But the common complications include:
- Respiratory Failure: It is a severe condition that makes it difficult to breathe on your own properly. It occurs when the lungs can’t get enough oxygen.
- Chronic Respiratory Impairment: It is a condition that occurs when the lungs cannot get enough oxygen into the blood or eliminate enough carbon dioxide from the body.
- Embolism: It is a blood clot that can be formed in any part of the body and can travel to the lung creating a block in the blood flow.
Conclusion
Identifying the cause of White Lung Pneumonia remains a complex challenge. The interplay of various factors, including bacterial and viral infections, environmental exposures and respiratory irritants, highlights the need for comprehensive research and continued efforts to enhance our understanding of this condition.
If you have trouble breathing or have a chronic cough, you may
Services
General Health
Frequently asked questions
Unfortunately, it is unknown whether white lung pneumonia is reversible.
The primary cause is viral or bacterial infections. However, it can also occur due to inhalation of substances like silica, asbestos, or other harmful particles.
Symptoms include shortness of breath, persistent coughing, chest pain, and fatigue. In severe cases, it can lead to respiratory failure.
Leave Comment
Services
Recommended for you

General Health
7 Skin-Loving Nutrients That Can Slow Down Ageing
Discover 7 essential skin-loving nutrients that can help slow down ageing naturally. Learn how these vitamins and minerals support youthful, radiant skin and promote long-term skin health.

General Health
Ampoxin 500 Capsule: Antibiotic Uses, Dosage, and Side Effects
Learn about Ampoxin 500 Capsule, a broad-spectrum antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections. Discover its composition, dosage, benefits, side effects, and important safety information.
_8.jpg?tr=q-85)
General Health
I got an ultrasound of my liver and the result came out to be Hepatomegaly with fatty liver(Grade 2). My doctor prescribed a few medicines for treatment. But online it says stop taking medicines as it can also affect the liver. Need help.
Subscribe
Sign up for our free Health Library Daily Newsletter
Get doctor-approved health tips, news, and more.

